Coconut-based soil
Coconut-based soil is now an excellent alternative to traditional peat-based substrates. The material is obtained from the processing of the coconut husk which, differently, would represent a processing waste of the food industry.
Features of coconut soil
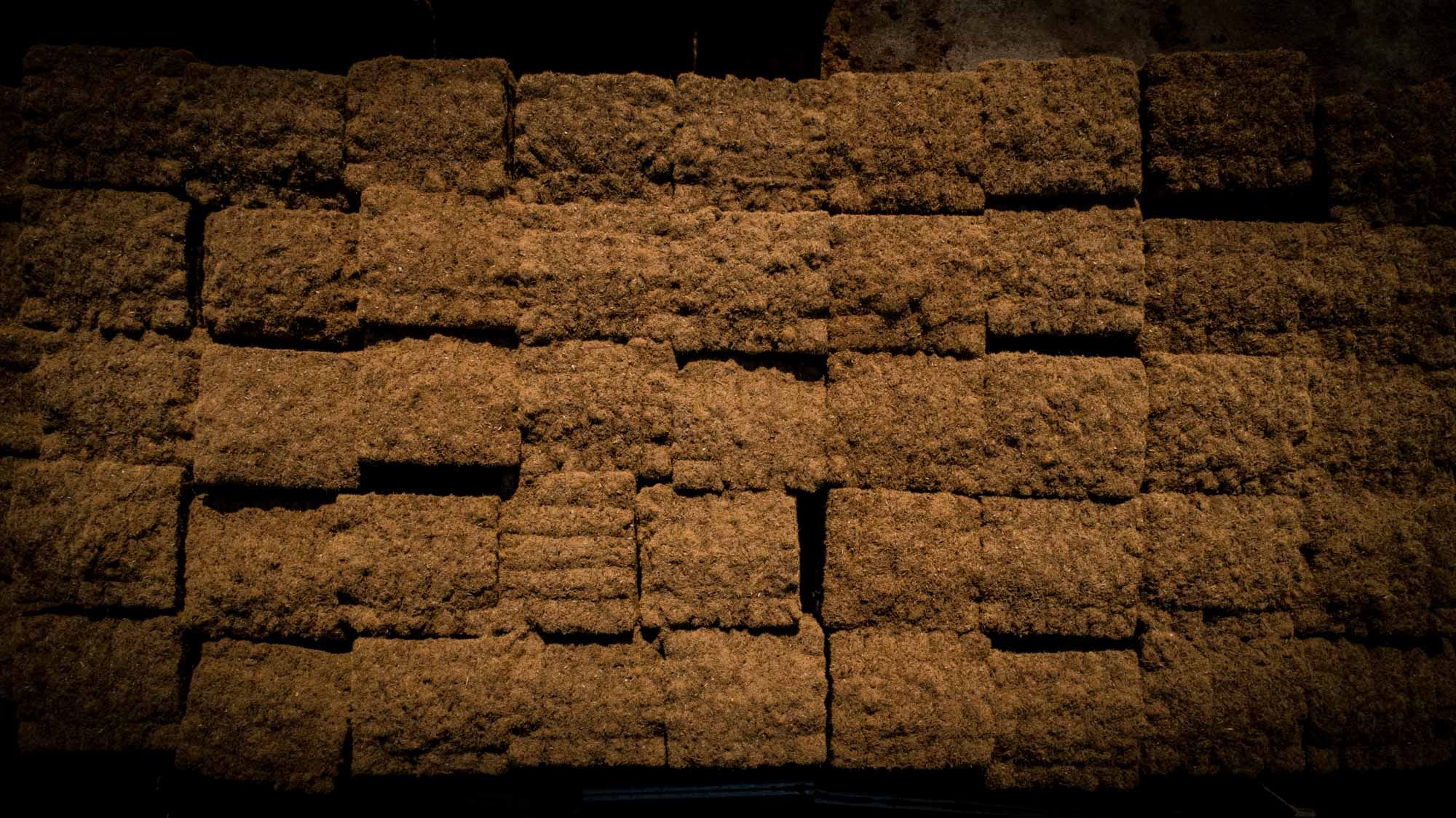
The resulting product is stable with Ph between 5.4 and 6.8 and very light (70-80 gr/lt), therefore easy to handle and transport. It has good water retention and a high volume of air that allows the roots to always have the right amount of water and oxygen. Unlike peat-based substrates, coconut soil is completely biodegradable and therefore has no disposal problems.
Coconut retains these chemical-physical characteristics for a long time, and for this reason it is also suitable for long cycle crops.
The particular advantages of coconut-based substrates can be summarized as follows:
-
Ability to create any recipe of your choice
-
Guarantee of the quality standard
-
Fast and capillary supply
-
Possibility to supply bulk material with trucks of different sizes or packed in big bags
Soil based on both coir pith and coir fibre guarantees a water retention that improves the exchange between water and air.
Soil based on Coir Pith
The pith or "coir peat" is the spongy part of the husk; it constitutes the "body" of the loam and has a great water retention.
Coir pith is a rather spongy product that allows plants to absorb more water and consequently obtain a good rooting and a good and constant oxygenation.
The characteristics of the soil based on coir pith
- is an organic material
- is light
- has good water retention
Soil based on coir fibre
Coir fiber is extracted from the processing of coconut, from that excess of material that would be destined for waste. Once extracted the fiber is washed.
It can be used both as a soil improver in soils and as a substrate in the crops of the floriculture and horticultural sectors.
The characteristics of the soil based on coconut fiber
- resistance to decomposition
- the stability of its structure over time
- very high porosity
Coconut fiber is widely used in the preparation of substrates for crops as they are very aerated; it is particularly suitable for the cultivation of ornamental plants.